
Bedside Assessment
With the help of radiological examinations, sampling can be made from almost all organs, especially thyroid, breast, lung and pancreas with fine needle Aspiration Biopsy (FNAB).
During this procedure, the pathologist makes a preliminary assessment at the bedside and reduces the risk of repeating the procedure due to inadequacy.

Cytological Examination
"Tissue" is not always required for pathological examination. Sometimes pathological diagnosis can be made without tissue, only by 'cell' sampling.
This method is most commonly used in the evaluation of "PAP smear", which is applied in cervical cancer screening. In addition, with the help of radiological examinations, cells can be sampled from tissues with a needle and in recent years, it can be used for almost all organs. With this method, which is defined as Fine Needle Aspiration Biopsy (FNAB), sampling can be performed from almost all organs, especially thyroid, breast, lung and pancreas. In the pathological examination part, these samples are spread on lams, stained and examined under a microscope. Cytological examination is also used in cancer screening tests, which can be applied by a very simple method in some cases. For instance; when the PAP smear result is reported as "Epithelial Cell Anomaly" or "Epithelial Cell Atypia", patient followed up begins and the treatment program is determined.


Frozen Section Examination (Intraoperative Diagnosis / Consultation)
Some urgent pathological examinations may be required to determine the course of the surgery.This "urgent" examination method, which allows the tissues to be examined by "freezing", is called "Frozen" Examination / Intraoperative Diagnosis-Consultation.
Surgical margin evaluation is used to determine whether there is metastasis in the lymph nodes, whether there is cancer in unexpected areas, and to determine the type, if any. After this procedure, routine pathological examination is continued. For example, by examining the presence of cancer spread in the axillary lymph nodes in a patient with breast cancer, the area of the surgery can be expanded. In bladder cancer, the surgery can be continued in a wider area depending on whether there is a tumor in the surgical margin / incision area.
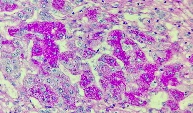
Histochemical Examination
PRoutine staining in pathology is Hematoxylin-Eosin stain. All biopsy specimens are first examined after this staining. In some cases, for instance;
special staining / histochemical examinations may be required in cases such as showing fungi, basal membrane in some kidney diseases, bacteria in case of doubt in gastric biopsies, etc.
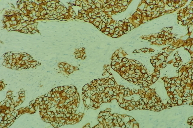
Immunohistochemical Examination
It is a method used to determine the origin of cells, especially in the diagnosis of cancer. In addition to the diagnosis, some examinations that will
determine the prognostic features of the disease are also in this group. It is also used to show the markers in cancer cells for determining "targeted therapy" options used in recent years.
Immunfluorescent Examination
It is a method used to determine the origin of cells, especially in the diagnosis of cancer and in kidney and skin diseases. In addition to the diagnosis, some examinations that will
determine the prognostic features of the disease are also in this group. It is also used to show the markers in cancer cells for determining "targeted therapy" options used in recent years.
Molecular Pathological Investigations
Molecular pathology is a field where anatomical pathology, clinical pathology and genetics work together.
Molecular pathology, which is also related to new fields of study (such as genomics, proteomics, metabolomics), which is referred to as OMICS, is mostly involved in cancer diagnosis and mutation analysis in daily practice.